User Inputs - Advanced (Activity-Specific)
The Advanced section contains areas for maintenance activity-specific inputs, organized by activity as shown below.
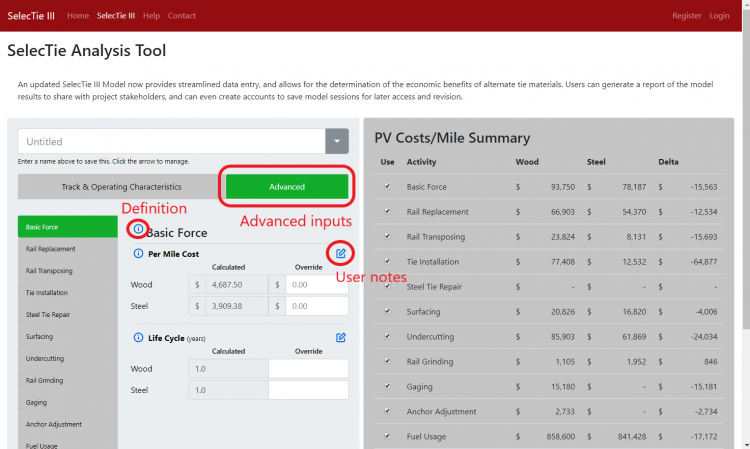
Basic Force
Basic Force is the basic labor cost and supplemental small material cost associated with routine annual upkeep of the track for each tie type. This cost can be neglected by un-checking the cost category in the Overall Results Summary. Inputs include:
- Per Mile Cost (Override): The Per Mile Cost of Basic Force. The Calculated costs are determined by the model based on relevant unit costs. The Calculated cost can be overridden by the user by inputting the user's specific costs into the Override field for each tie type.
- Life Cycle (Override): The Basic Force life cycle (typically annual). The Calculated Life Cycle is determined by the model based on track and traffic parameters input by the user. The user can input specific life cycles based on their experience in the Override field. Note that Basic Force is an annual event and should remain 1 for each tie type.
Rail Replacement
Rail Replacement is the fully burdened labor, material and equipment costs associated with the replacement of both rails. This cost is annualized based on the rail replacement cycle for each tie type. This cost can be neglected by un-checking the cost category in the Overall Results Summary. Inputs include:
- Rail Weight: The predominant weight of the rail on the track segment being analyzed in pounds per yard (lb/yard).
- Rail Metallurgy: The metallurgy of the predominant weight of the rail on the track segment being analyzed in pounds per yard (lb/yard). Select Standard or Premium. This affects the life of the rail.
- Lubrication: The level of lubrication of the rail on the track segment. This strongly affects rail life and as such should be defined specifically for smaller segments (curves) or specified as an average for a long track segment. Select None, Moderate, or Well.
- Jointed or Welded Track: The rail connection used on the track segment. Select CWR (Continuously Welded Rail) or Jointed. All track will generally have joints and welds. This field is associated with the predominant rail connection type.
- Per Mile Cost (Override): The Per Mile Cost of Rail Replacement. The Calculated costs are determined by the model based on relevant unit material, labor and equipment costs. The Calculated cost can be overridden by the user by inputting the user's specific costs for Rail Replacement into the Override field for each tie type.
- Life Cycle (Override): The Rail Replacement Cycle for each tie type. The Calculated Life Cycle is determined by the model based on track and traffic parameters input by the user, as well as the rail parameters input. The user can input specific Rail life (Replacement) cycles based on their experience in the Override field.
Rail Transposing
Rail Transposing is the fully burdened labor, material and equipment costs associated with transposing the rails; swapping or inverting the left and right rails to take advantage of the material available on the field side of the rail. This cost is annualized based on 50% of the rail replacement cycle for each tie type. This cost can be neglected by un-checking the cost category in the Overall Results Summary. Inputs include:
- Per Mile Cost (Override): The Per Mile Cost of Rail Transposing. The Calculated costs are determined by the model based on relevant unit material, labor and equipment costs. The Calculated cost can be overridden by the user by inputting the user's specific costs for Rail Transposing into the Override field for each tie type.
- Life Cycle (Override): The Rail Transposing Cycle for each tie type. The Calculated Rail Transposing Cycle is determined by the model based on track and traffic parameters input by the user, as well as the rail parameters input (calculated as 50% of the Rail Replacement cycle). The user can input specific Rail Transposing cycles based on their experience in the Override field.
Tie Installation
Tie Installation is the fully burdened labor, material (including fasteners) and equipment costs associated with the replacement of each tie type. This cost is annualized based on the tie life cycle for each tie type. This cost can be neglected by un-checking the cost category in the Overall Results Summary. Inputs include:
- Width: The Width of each tie type in inches (in).
- Height: The Height of each tie type in inches (in).
- Length: The Length of each tie type in feet (ft).
- Spacing: The Spacing of each tie type in inches (in). Used to determine the number of ties per mile.
- Number of Wood Ties Replaced Each Cycle: Average number of wood ties replaced per mile during a major tie renewal program, i.e., the Wood Tie Life Cycle.
- Per Mile Cost (Override): The Per Mile Cost of Tie Installation. The Calculated costs are determined by the model based on relevant unit material, labor and equipment costs. The Calculated cost can be overridden by the user by inputting the user's specific costs for Tie Installation into the Override field for each tie type.
- Life Cycle (Override): The Tie Installation Cycle for each tie type. The Calculated Life Cycle is determined by the model based on track and traffic parameters input by the user, as well as the tie parameters input. The user can input specific Tie Life cycles based on their experience in the Override field.
Concrete Tie Repair
Concrete Tie Repair is the fully burdened labor, material and equipment costs associated with the repair of concrete ties in a mile due to rail seat abrasion. This cost is annualized based on the Concrete Tie Repair cycle and the percentage of ties that require repair (based on probability). This cost can be neglected by un-checking the cost category in the Overall Results Summary. Inputs include:
- Probability of Rail Seat Abrasion: The probability of rail seat abrasion occurring. This value is used to determine the amount of Concrete Tie Repair for a given mile.
- Per Mile Cost (Override): The Per Mile Cost of Concrete Tie Repair for 100% of the concrete ties in a mile. The Calculated costs are determined by the model based on relevant unit material, labor and equipment costs and the percentage of ties experiencing rail seat abrasion. The Calculated cost can be overridden by the user by inputting the user's specific costs for Concrete Tie Repair into the Override field.
- Life Cycle (Override): The Concrete Tie Repair Cycle. The Calculated Life Cycle is determined by the model based on track and traffic parameters input by the user, as well as the concrete tie parameters input. The user can input a specific Concrete Tie Repair cycle based on their experience in the Override field.
Surfacing
Surfacing is the fully burdened labor, material and equipment costs associated with production surfacing of the track. This cost is annualized based on the Surfacing cycle for each tie type. This cost can be neglected by un-checking the cost category in the Overall Results Summary. Inputs include:
- Ballast Specific Gravity: Specific Gravity of the ballast in tons per cubic yard (tons/cubic yard).
- Surface Lift: The typical lift of the track during production surfacing operations in inches (in).
- Ballast Depth Below Tie: Depth of ballast below a wood tie in inches (in).
- Ballast Condition: Typical condition of the ballast. Select Clean or Fouled. This affect the surfacing cycle.
- Per Mile Cost (Override): The Per Mile Cost of Surfacing the track. The Calculated costs are determined by the model based on relevant unit material, labor and equipment costs. The Calculated cost can be overridden by the user by inputting the user's specific costs for Surfacing into the Override field for each tie type.
- Life Cycle (Override): The Surfacing Cycle for each tie type. The Calculated Life Cycle is determined by the model based on track and traffic parameters input by the user for each tie type. The user can input specific Tie Life cycles based on their experience in the Override field.
Undercutting
Undercutting is the fully burdened labor, material and equipment costs associated with production Undercutting of the track. This cost is annualized based on the Undercutting cycle for each tie type. This cost can be neglected by un-checking the cost category in the Overall Results Summary. Inputs include:
- Undercutting Depth: Average depth of undercutting to clean the ballast in inches (in).
- Per Mile Cost (Override): The Per Mile Cost of Undercutting the track. The Calculated costs are determined by the model based on relevant unit material, labor and equipment costs. The Calculated cost can be overridden by the user by inputting the user's specific costs for Undercutting into the Override field for each tie type.
- Life Cycle (Override): The Undercutting Cycle for each tie type. The Calculated Life Cycle is determined by the model based on track and traffic parameters input by the user for each tie type. The user can input specific Undercutting cycles based on their experience in the Override field.
Rail Grinding
Rail Grinding is the fully burdened labor and equipment costs associated with production Grinding of the rail (typically by contract grinding). This cost is annualized based on the Rail Grinding cycle for each tie type. This cost can be neglected by un-checking the cost category in the Overall Results Summary. Inputs include:
- Per Mile Cost (Override): The Per Mile Cost of Grinding the rail. The Calculated costs are determined by the model based on relevant unit material, labor and equipment costs. The Calculated cost can be overridden by the user by inputting the user's specific costs for Rail Grinding into the Override field for each tie type.
- Life Cycle (Override): The Rail Grinding Cycle for each tie type. The Calculated Life Cycle is determined by the model based on track and traffic parameters input by the user for each tie type. The user can input specific Rail Grinding cycles based on their experience in the Override field.
Gaging
Gaging is the fully burdened labor, material and equipment costs associated with regaging the track (moving the rails on the same ties) and repairing the spike holes for wood ties. This cost is annualized based on the Gaging cycle. This cost can be neglected by un-checking the cost category in the Overall Results Summary. Inputs include:
- Per Mile Cost (Override): The Per Mile Cost of Gaging the entire mile of wood tie track. The Calculated costs are determined by the model based on relevant unit material, labor and equipment costs. The Calculated cost can be overridden by the user by inputting the user's specific costs for Gaging into the Override field.
- Life Cycle (Override): The Gaging Cycle for wood ties. The Calculated Life Cycle is determined by the model based on track and traffic parameters input by the user for wood ties. The user can input specific Gaging cycles based on their experience in the Override field.
Anchor Adjustment
Anchor Adjustment is the fully burdened labor, material and equipment costs associated with adjusting the anchors for wood tie track. This cost is annualized based on the Anchor Adjustment cycle. This cost can be neglected by un-checking the cost category in the Overall Results Summary. Inputs include:
- Per Mile Cost (Override): The Per Mile Cost of Anchor Adjustment for the entire mile of wood tie track. The Calculated costs are determined by the model based on relevant unit material, labor and equipment costs. The Calculated cost can be overridden by the user by inputting the user's specific costs for Anchor Adjustment into the Override field.
- Life Cycle (Override): The Anchor Adjustment Cycle for wood ties. The Calculated Life Cycle is determined by the model based on track and traffic parameters input by the user for wood ties. The user can input specific Anchor Adjustment cycles based on their experience in the Override field.
Fuel Usage
Fuel Usage is the fully burdened Fuel costs associated with operations on each type (tie) of track. This cost is annualized based on the annual amount of fuel usage for each tie type. This cost can be neglected by un-checking the cost category in the Overall Results Summary. Inputs include:
- Percentage Fuel Savings: The percentage of fuel savings for the alternate tie material (savings over wood tie track).
- Average Number of Power Units: Average number of locomotives per train.
- Average Power per Unit: Average power associated with the locomotive in horsepower (hp).
- Average Fuel Usage: Average fuel usage for each locomotive in gallons per thousand horsepower hours (gal/1000-hp-hr).
- Average Train Weight: Average weight of a train in tons.
- Per Mile Cost (Override): The Per Mile Cost of Fuel. The Calculated costs are determined by the model based on relevant fuel costs and specific locomotive characteristics and traffic for the track segment for each tie type. The Calculated cost can be overridden by the user by inputting the user's specific costs into the Override field for each tie type.
- Life Cycle (Override): The Fuel Usage life cycle (typically annual). The user can input specific life cycles based on their experience in the Override field. Note that Fuel Usage is an annual event and should remain 1 for each tie type.
Derailment
Derailment is the fully burdened labor, material and equipment costs associated with repair of the track after a derailment occurs. This cost is annualized based on the probability of a derailment occurring and the length of track damaged after a potential (based on probability) derailment for each type of track (tie). This cost can be neglected by un-checking the cost category in the Overall Results Summary. Inputs include:
- Probability of Derailment: The probability a derailment will occur on each type of track (tie).
- Average Length of Derailment: The average length of track that will be damaged when a derailment occurs for each type of track (tie) in feet (ft).
- Per Mile Cost (Override): The Per Mile Cost of Repairing an entire mile of track after a derailment. The Calculated costs are determined by the model based on relevant unit material, labor and equipment costs. The Calculated cost can be overridden by the user by inputting the user's specific costs for repair due to a derailment into the Override field for each tie type.
- Life Cycle (Override): The Derailment life cycle (typically annual). The user can input specific life cycles based on their experience in the Override field. Note that Derailment is an annual event (based on probability) and should remain 1 for each tie type.
Conversion to Alternate Ties
The Conversion to Alternate Ties is a one time cost associated with upgrading an existing wood tie track to an alternate tie material. This cost is the fully burdened labor, material and equipment costs associated with converting the track and includes disposal costs. Inputs include:
- Per Mile Cost (Override): The Per Mile Cost of Converting an entire mile of track from wood ties to an alternate tie material. The Calculated costs are determined by the model based on relevant unit material, labor and equipment costs. The Calculated cost can be overridden by the user by inputting the user's specific costs for converting the track into the Override field for each tie type.
Return to main Help page.